Acne Prone Skin
How To Treat Your Acne Prone Skin And What Products To Use For It
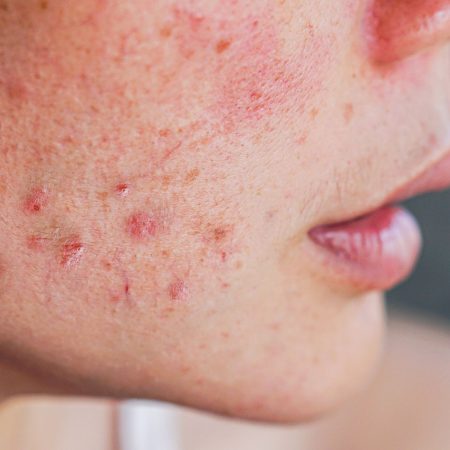
Acne-prone skin refers to a skin type that is more susceptible to developing acne, a common skin condition characterized by the presence of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and occasional cysts or nodules. Acne occurs when the hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria, leading to inflammation and the formation of various types of acne lesions.
Several factors contribute to acne-prone skin, including:
Excessive sebum production: People with acne-prone skin tend to produce more sebum (oil) than necessary, which can contribute to clogged pores.
Hyperkeratinization: The cells lining the hair follicles can become sticky and combine with sebum, forming plugs that block the follicles.
Bacterial activity: The Propionibacterium acnes bacteria, which naturally reside on the skin, can multiply within clogged pores, leading to inflammation and acne breakouts.
Hormonal fluctuations: Hormonal changes, especially during puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy, can trigger acne development by stimulating sebum production.
Genetic predisposition: Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to acne, meaning they are more likely to develop the condition due to inherited factors.
Treating acne-prone skin involves a combination of gentle skincare practices, targeted treatments, and, in some cases, professional guidance. Here are some tips on how to treat acne-prone skin:
Gentle Cleansing:
Use a mild, fragrance-free cleanser to wash your face twice a day. Avoid harsh cleansers that can strip the skin of its natural oils, as this can trigger the overproduction of sebum.
Non-Comedogenic Products:
Choose skincare and makeup products labeled as “non-comedogenic” to prevent pore clogging.
Moisturize:
Even if your skin is oily, it’s essential to use a lightweight, oil-free, and non-comedogenic moisturizer. Keeping the skin hydrated helps maintain a healthy barrier.
Salicylic Acid:
Incorporate a salicylic acid-based product into your routine. Salicylic acid exfoliates the skin, unclogs pores, and helps reduce inflammation. Start with a lower concentration and gradually increase if needed.
Benzoyl Peroxide:
Benzoyl peroxide is effective against acne-causing bacteria and can be found in cleansers, spot treatments, and leave-on products. Start with a lower concentration to minimize irritation.
Retinoids (Retinol, Tretinoin):
Retinoids help promote cell turnover, unclog pores, and reduce the appearance of acne scars. Start with a lower concentration, and use them at night. Use caution if your skin is sensitive, and consult a dermatologist.
Tea Tree Oil:
Tea tree oil has natural antibacterial properties. Dilute it with a carrier oil and apply it sparingly to affected areas. Be cautious, as some individuals may be sensitive to it.
Use Sunscreen:
Always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30, especially when using acne-fighting products. Some acne treatments can increase sensitivity to the sun.
Avoid Touching Your Face:
Refrain from touching or picking at your face, as it can worsen acne and lead to scarring.
Cleanse After Exercise:
If you sweat, cleanse your face after exercise to prevent sweat and oil buildup, which can contribute to acne.
Change Pillowcases Regularly:
Change your pillowcases regularly to avoid transferring oils and bacteria to your face while sleeping.
Healthy Diet:
Maintain a well-balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole foods. Some studies suggest a link between diet and acne.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink enough water to keep your skin hydrated and promote overall health.
Consult a Dermatologist:
If over-the-counter products are not effective, or if your acne is severe, consult a dermatologist. They can prescribe stronger medications and provide personalized advice.
Consider Professional Treatments:
Professional treatments like chemical peels, laser therapy, or microdermabrasion can be considered for more severe cases. Consult with a dermatologist to determine the best options for your skin.
It’s important to note that what works for one person may not work for another. If you have persistent or severe acne, seeking professional advice is crucial to develop a personalized treatment plan. Be patient and consistent with your skincare routine, and avoid the temptation to use aggressive products that can exacerbate the problem.
Here are some steps and recommended products to follow for acne-prone skin:
Step 1
Cleanse
Cleanse: Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser twice a day to help remove excess oil, dirt, and makeup from your skin. Look for cleansers that contain salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide, as they can help unclog pores and prevent breakouts. Some recommended products for this step are:
Step 2
Toner
Tone: Using a toner after cleansing can help remove any remaining dirt and oil, balance your skin’s pH, and prep your skin for other products. Look for toners that are alcohol-free and contain ingredients like witch hazel, glycolic acid, or tea tree oil. Some recommended products for this step are:
Step 3
Treat
Treat: Acne-prone skin can benefit from using targeted treatments to help control breakouts. Look for products that contain active ingredients like salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, or retinoids. Some recommended products for this step are:
Step 4
Moisturize
Moisturize: Even if you have oily skin, it’s important to use a moisturizer to help keep your skin hydrated and healthy. Look for non-comedogenic, lightweight formulas that won’t clog your pores. Some recommended products for this step are:
Step 4
Protect
Protect: Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen daily is essential to protect your skin from sun damage and prevent post-acne marks from darkening. Look for oil-free, non-comedogenic formulas with at least SPF 30. Some recommended products for this step are:
BEAUTY OF JOSEON – Relief Sun : Rice + Probiotics Set SPF50+ PA++++
La Roche-Posay Anthelios Clear Skin Oil-Free Sunscreen SPF 60
Isntree Hyaluronic Acid Watery Sun Gel Sunscreen, SPF 50+ PA++++
Remember to patch-test new products before using them all over your face and to consult with a dermatologist if you have severe or persistent acne.
- Categories
- Skin Type
















